Anti-Depressants
| Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
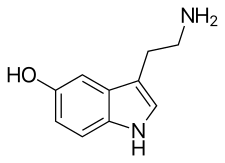
Serotonin, the neurotransmitter that is involved in the mechanism of action of SSRIs. |
|
| Class identifiers | |
| Synonyms | Serotonin-specific reuptake inhibitors, serotonergic antidepressants[1] |
| Use | Major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders |
| ATC code | N06AB |
| Biological target | Serotonin transporter |
| Clinical data | |
| Drugs.com | Drug Classes |
| Consumer Reports | Best Buy Drugs |
| External links | |
| MeSH | D017367 |
| In Wikidata | |
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
SSRIs increase the extracellular level of the neurotransmitter serotonin by limiting its reabsorption (reuptake) into the presynaptic cell.[2] They have varying degrees of selectivity for the other monoamine transporters, with pure SSRIs having strong affinity for the serotonin transporter and only weak affinity for the norepinephrine and dopamine transporters.
SSRIs are the most widely prescribed antidepressants in many countries.[3] The efficacy of SSRIs in mild or moderate cases of depression has been disputed and may or may not be outweighed by side effects, especially in adolescent populations.[4][5][6][7]