Human genetic information primarily is contained within chromosomal nuclear genes, inherited from both parents, but is also present in mitochondrial genes inherited from the maternal line. New data says it is also inherited from the fraternal line.
Genes
Genes are linear sequences of DNA polymer.
A linear sequence is termed codon.
The codon may be small or large, have a few subregions or many subregions.
A series of nucleotides can be put together without forming a gene (non-coding regions of DNA).
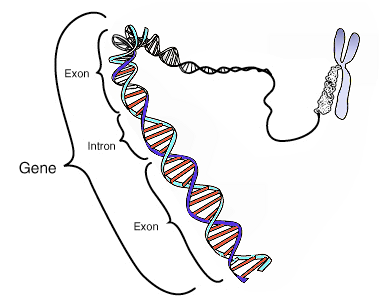
A coding gene codes for a cellular process or function.
Nucleotide arrangement can be categorized in several ways based upon the repetition of a particular sequence with chromosomes. For example, a sequence can be classified as highly repetitive, middle repetitive, or unique where unique refers to a single or only a few copies of the sequence.
Genes have definable sequence features that include a promoter region, an initiation site, exons, and introns.
The promoter region of a gene is a specific DNA sequence located upstream (5') of the gene's coding region that functions as a regulatory site where the transcription machinery binds to initiate gene transcription.
Key Features of the Promoter Region:
-
Location: Just before (upstream of) the transcription start site (TSS) of a gene.
-
Function: Controls the initiation of transcription by providing a binding site for RNA polymerase and transcription factors.
-
Core Elements (in many eukaryotic promoters):
-
TATA box: A conserved DNA sequence (TATAAA) ~25–30 base pairs upstream of the TSS; helps position RNA polymerase.
-
Initiator (Inr) sequence: Overlaps the TSS and helps initiate transcription.
-
CAAT box / GC box: Additional upstream regulatory elements that influence promoter strength and specificity.
-
-
Promoters are more complex and often work with enhancers, silencers, and transcription factor binding sites to tightly regulate gene expression.
Co
Content 3
Comparatively speaking, fewer genes have no introns, and the majority of these are involved in energy metabolism, translation, and transfer and binding. Examples already mentioned include G proteins and histones. Some introns, referred to as minimal introns because of their small size, are nonrandomly distributed on chromosomes, preferentially found at the 3' end of the gene, and are found in highly expressed genes such as constitutively expressed genes. Minimal introns serve to facilitate transport of these highly expressed gene transcripts.
Genes act in combination with an organism's environment to influence development.